How did Instacart use AI to grow their business?
A practical breakdown of their strategy that any service business can copy.
Hey Adopter,
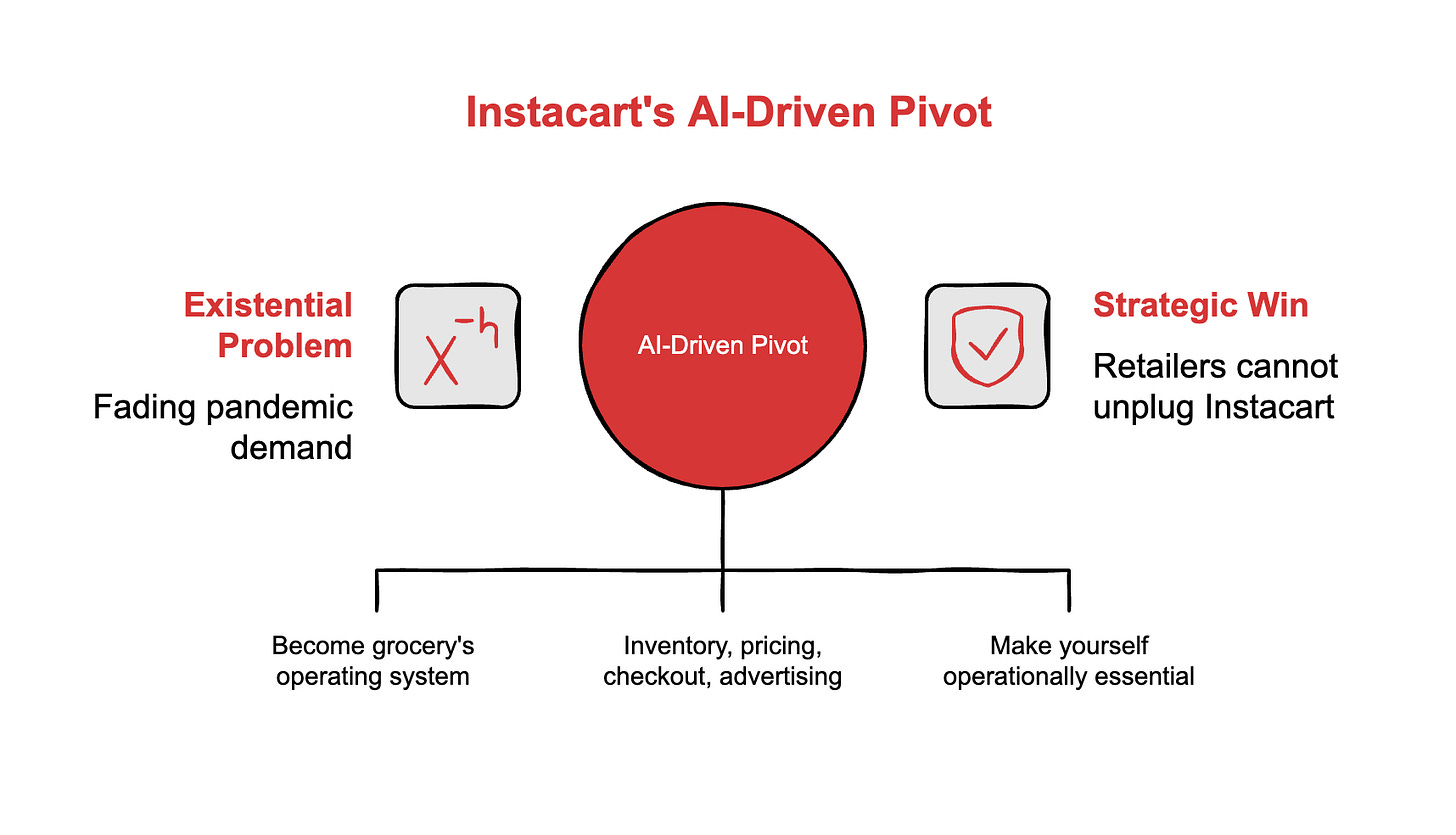
Between 2020 and 2025, Instacart faced an existential problem. Pandemic demand was fading. Retailers were building their own delivery. The low-margin delivery model was a dead end.
Their response was not to deliver groceries faster. It was to stop being a delivery company entirely. By 2025, Instacart had repositioned as the “operating system” for North American grocery, with AI at the centre of inventory, pricing, checkout, and advertising. The lesson for SMBs is not about scale. It is about integration depth and making yourself operationally essential.
The result that changes the SMB playbook
Instacart’s AI-driven pivot delivered a 127% earnings surprise in Q2 2025. Gross margins climbed from roughly 50% to 70%. Their advertising business became the primary profit driver, built entirely on AI-powered relevance models. But the strategic win was simpler: retailers cannot unplug Instacart without breaking their own operations.
Download the full case study for the stack, timelines, and measured impact.
Over 60% engineering adoption of their internal AI assistant within one year
70,000 lines of code generated monthly through AI-assisted development
$350 million acquisition of Caper AI to capture offline behavioural data
15% to 100% incremental sales lift for advertising partners
70% increase in prepared food orders after deploying their order management integration
What SMBs can use this week
Instacart built an internal “Prompt Exchange” where employees share effective AI prompts across teams. This created a flywheel for AI literacy without formal training programmes. Any SMB can replicate this with a shared channel or document.
The data you actually need
Their smart carts capture what shoppers pick up, put back, and buy. The insight: your AI is only as good as your behavioural data. Before investing in models, map where customer decisions happen and whether you are capturing that signal.
Warning signs from the case
Identical products were priced up to 23% differently for different users. The FTC launched an investigation. AI-powered pricing without transparency creates regulatory and reputational risk. Document your logic before optimising margins.